Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), as a complex chronic intestinal disease, involves multiple factors such as genetics, immunity, and environment in its pathogenesis. Choosing appropriate animal models is crucial in the development of IBD drugs. Among them, the IBD model induced by DSS (sodium dextran sulfate) has become one of the most commonly used research tools due to its simple operation and good reproducibility.
The mechanism of action of DSS model
DSS is a sulfated polysaccharide that can cause damage to mouse colon epithelial cells when administered through drinking water. Its mechanism of action mainly includes:
• Direct cytotoxicity:Disrupting the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier
• immune activation:Promote macrophage infiltration and release of inflammatory factors
• Dysbiosis of microbiota:Change the composition of gut microbiota
The clinical similarity between DSS model and human IBD
Highly consistent pathological features
• The patterns of mucosal ulcers and epithelial damage are highly similar to those of human ulcerative colitis (UC)
• The infiltration characteristics of inflammatory cells are consistent with clinical biopsy specimens
• Intestinal barrier dysfunction is the core pathological link of IBD
Correspondence between clinical symptoms
• Weight loss → malnutrition in human IBD patients
• Hematochezia and diarrhea → Main clinical symptoms
• Disease Activity Index (DAI) → Clinical Disease Activity Index Evaluation
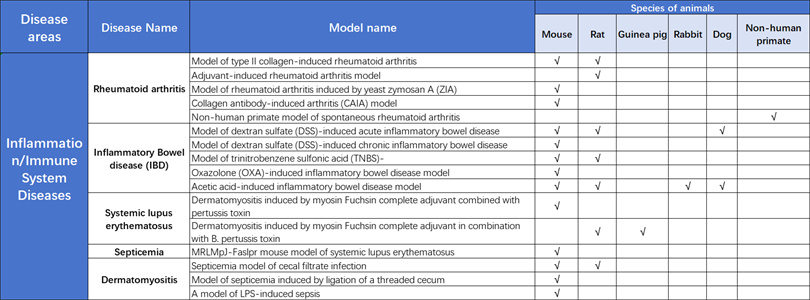
KCI Biotech Inflammation/Immune System Disease Pharmacological and Pharmacological Evaluation Platform
The KCI Biotech Inflammation/Immune System Disease Pharmacology and Pharmacology Evaluation Platform has a comprehensive animal model system and has accumulated rich project experience to meet diverse research needs. At present, the company has established extensive long-term cooperation with many well-known pharmaceutical companies and research institutions at home and abroad, providing a solid foundation for the development of innovative drugs.
DSS induced IBD animal model case sharing
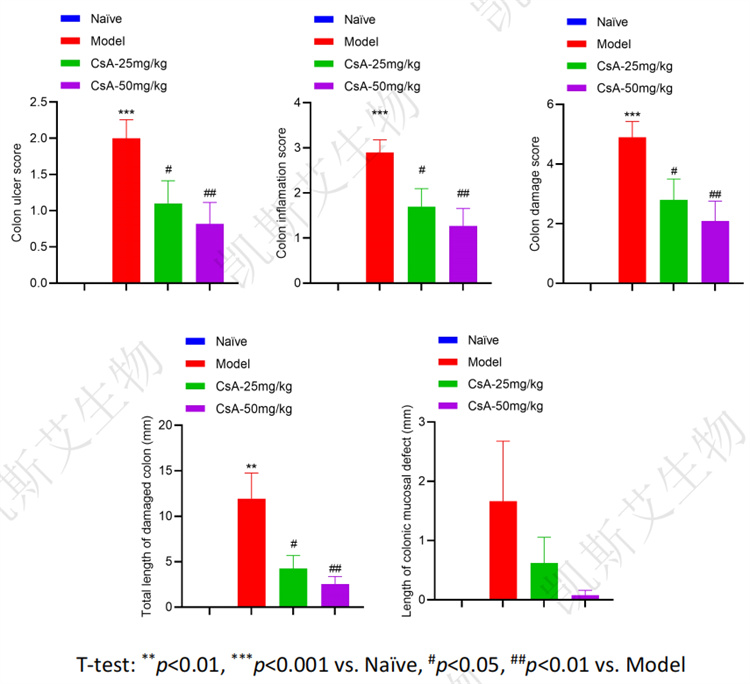
01 DSS induced acute IBD model in mice
data display
• Changes in Disease Activity Indicators&Colonic Gross Measurement

• Pathological examination results of colon tissue


A small amount of scattered T lymphocytes (red arrow) can be seen in the normal colonic mucosal layer; A large number of T lymphocytes can be seen infiltrating the colon ulcer site in the model animal (green arrow); Low dose CsA treatment showed a significant reduction in T cell infiltration at the ulcer site (green arrow); High dose CsA treatment showed a significant reduction in T cell infiltration at the ulcer site (green arrow).

A small amount of macrophages (red arrow) are scattered in the normal colonic mucosal layer; A large number of macrophages can be seen infiltrating the colon ulcer site in the model animal (green arrow); Low dose CsA treatment showed a significant reduction in macrophage infiltration at the ulcer site (green arrow); High dose CsA treatment showed a significant reduction in macrophage infiltration at the ulcer site (green arrow).
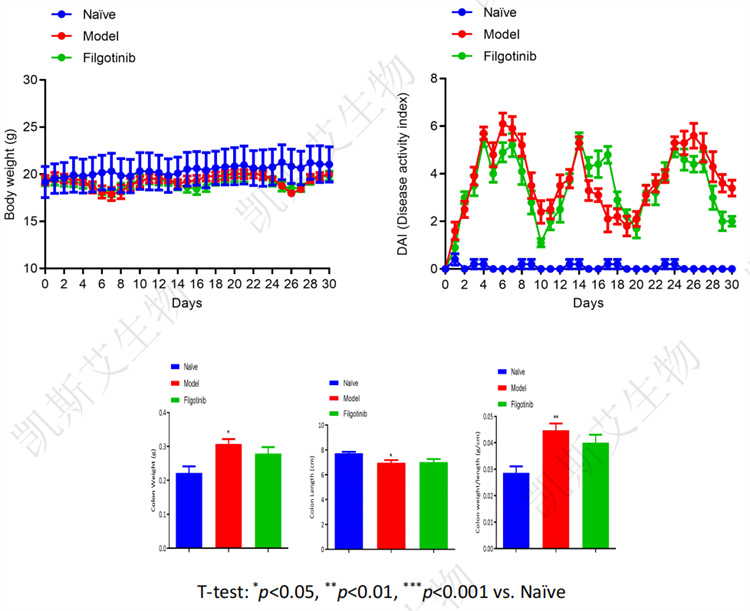
02 DSS induced chronic IBD model in mice
data display• Changes in Disease Activity Indicators&Colonic Gross Measurement
• Pathological examination results of colon tissue (HE staining)
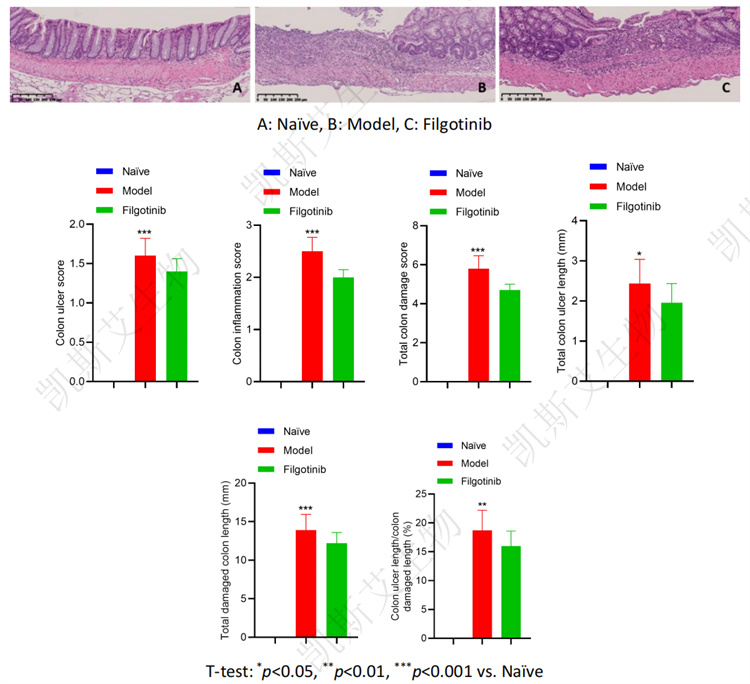
03 DSS induced acute IBD model in rats
data display• Changes in Disease Activity Indicators&Colonic Gross Measurement
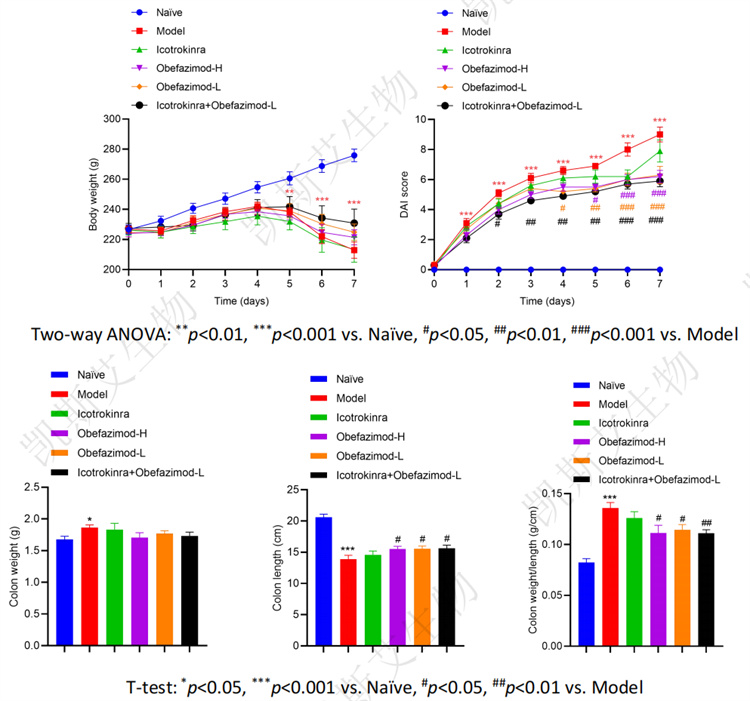
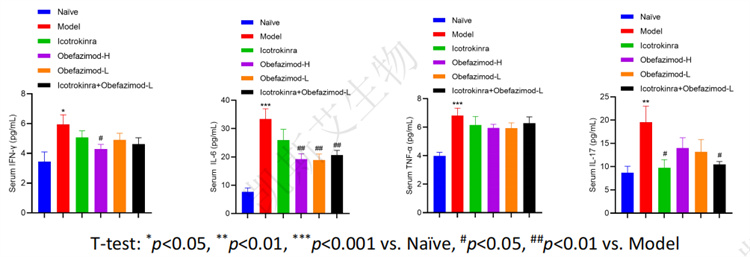
• Changes in serum cytokine levels and colon cytokine levels